Create fixtures
To insert some data into the database, we will use fixtures. Fixtures are a way to insert data into the database. The fixtures are defined in the db/fixtures/generators directory in the api directory. To generate fixtures, it's often useful to generate a lot of data. @faker-js/faker is often a good choice for generating a lot of random data.
Create Fixtures
Create a new service in the fixtures/generators directory with the following content:
import { faker } from "@faker-js/faker";
import { InjectRepository } from "@mikro-orm/nestjs";
import { EntityManager, EntityRepository } from "@mikro-orm/postgresql";
import { Injectable, Logger } from "@nestjs/common";
import { Customer } from "@src/customers/entities/customer.entity";
@Injectable()
export class CustomersFixtureService {
private logger = new Logger(CustomersFixtureService.name);
constructor(
private readonly entityManager: EntityManager,
@InjectRepository(Customer) private readonly repository: EntityRepository<Customer>,
) {}
async generate(): Promise<void> {
this.logger.log("Generating customers...");
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
const customer = this.repository.create({
id: faker.string.uuid(),
firstName: faker.person.firstName(),
lastName: faker.person.lastName(),
});
this.entityManager.persist(customer);
}
}
}
Add Fixtures to the FixturesCommand
Additionally, the created fixtures must be executed.
Open db/fixtures/fixtures.command.ts and call the service:
export class FixturesCommand extends CommandRunner {
constructor(
//...
private readonly customersFixtureService: CustomersFixtureService,
) {
super();
}
async run(): Promise<void> {
//...
await this.customersFixtureService.generate();
await this.orm.em.flush();
}
}
Execute Fixtures
Everything should be set up now. To execute the fixtures, run the following command:
cd api
npm run fixtures
Verify Fixtures
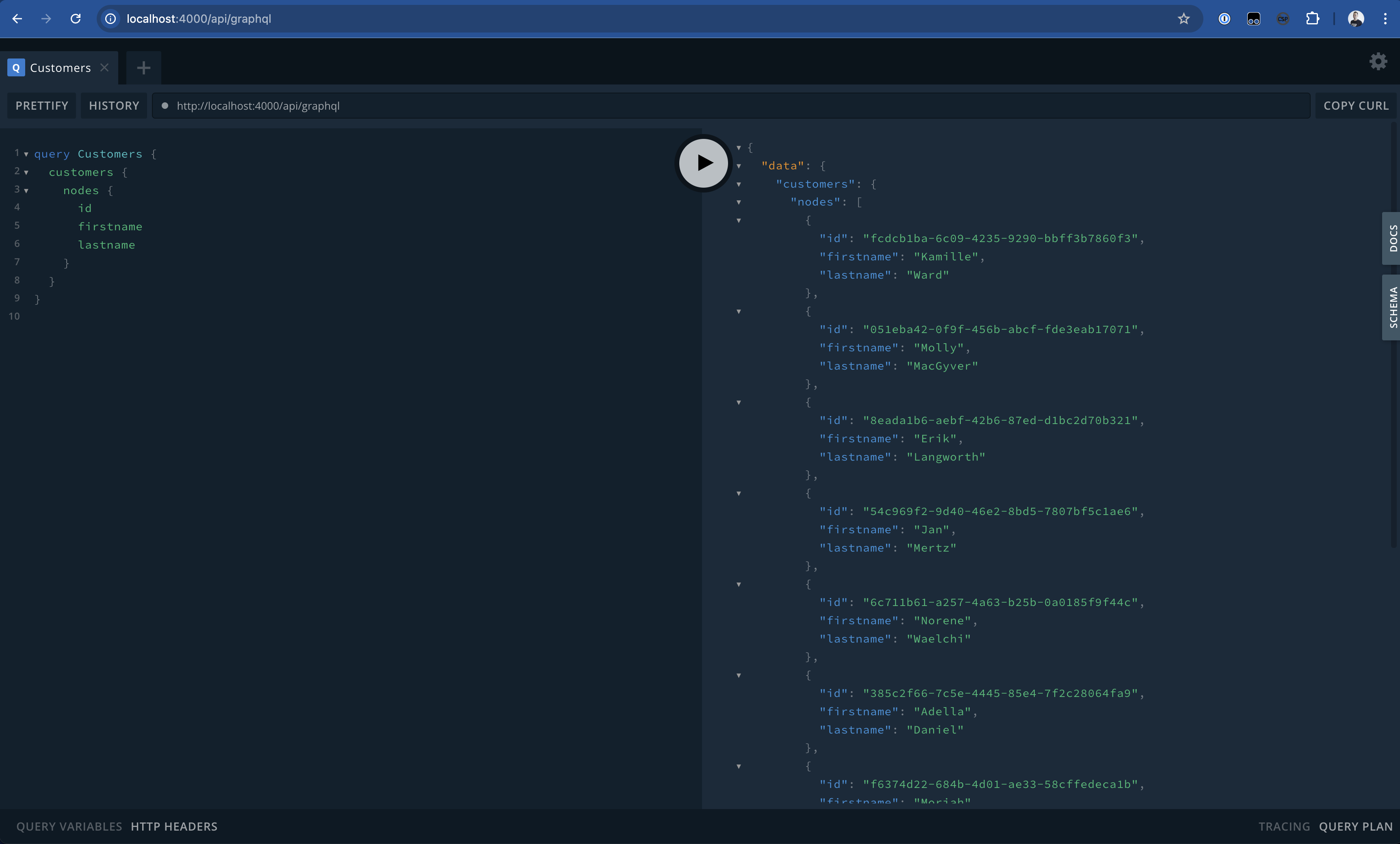
Now we are ready to execute the Query again in the GraphQL Playground, and one should see that the Query is executed successfully and will return the generated Data.