API Entity with CRUD Generator
Generating an entity with the API-Generator
Since we are building the API first, we will start by generating a new entity. Navigate to the api folder and create a new directory, for example, api/src/customer. Inside this directory, create a new file customer.entity.ts with the following content:
import { CrudField, CrudGenerator } from "@comet/cms-api";
import { BaseEntity, Entity, PrimaryKey, Property } from "@mikro-orm/core";
import { Field, ID, ObjectType } from "@nestjs/graphql";
import { v4 } from "uuid";
@Entity()
@ObjectType()
@CrudGenerator({ targetDirectory: `${__dirname}/../generated/`, requiredPermission: "customer" })
export class Customer extends BaseEntity<Customer, "id"> {
@CrudField({ search: true, filter: true, sort: true, input: false })
@Field(() => ID)
@PrimaryKey({ columnType: "uuid" })
id: string = v4();
@CrudField({ search: true, filter: false, sort: false, input: true })
@Field()
@Property({ columnType: "text" })
firstName: string;
@CrudField({ search: true, filter: false, sort: false, input: true })
@Field()
@Property({ columnType: "text" })
lastName: string;
@CrudField({ search: false, filter: false, sort: false, input: false })
@Property({ onUpdate: () => new Date() })
@Field()
updatedAt?: Date = new Date();
}
If the API Generator is setup correctly, adding the entity should generate multiple files in the specified ../generated output directory.
Review the Setup API Generator section on how to setup the generator correctly.
Alternatively, you can run the generator manually:
cd api
npm run api-generator
The API Generator will generate multiple files inside the specified ../generated output directory. It will contain a customer.resolver.ts and some DTO-related files (customer.filter.ts, customer.input.ts, customer.sort.ts, customer.args.ts, paginated-customer.ts).
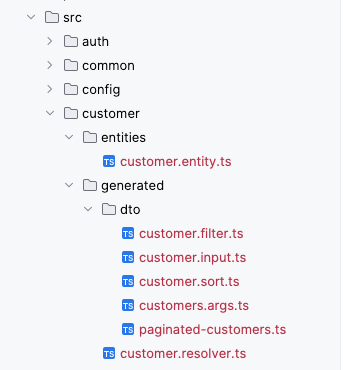
To integrate the new entity into the application, you have to add a new NestJS module. Create a new file customer.module.ts in the api/src/customer directory with the following content:
import { MikroOrmModule } from "@mikro-orm/nestjs";
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { Customer } from "./entities/customer.entity";
import { CustomerResolver } from "./generated/customer.resolver";
@Module({
imports: [MikroOrmModule.forFeature([Customer])],
providers: [CustomerResolver],
})
export class CustomerModule {}
This generated module must be added to the api/src/app.module.ts and registered.
import { DynamicModule, Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { CustomerModule } from "@src/customer/customer.module";
import { DbModule } from "@src/db/db.module";
import { ContentScope as BaseContentScope } from "@src/site-configs";
import { Config } from "./config/config";
import { ConfigModule } from "./config/config.module";
@Module({})
export class AppModule {
static forRoot(config: Config): DynamicModule {
return {
module: AppModule,
imports: [ConfigModule.forRoot(config), DbModule, CustomerModule],
};
}
}
//...
As soon as the new CustomerModule is registered in the app module, the schema will update and provide the new generated Queries/Mutations, including the Object types and necessary inputs.
type Customer {
id: ID!
firstName: String!
lastName: String!
updatedAt: DateTime!
}
type PaginatedCustomers {
nodes: [Customer!]!
totalCount: Int!
}
input CustomerFilter {
id: StringFilter
and: [CustomerFilter!]
or: [CustomerFilter!]
}
input CustomerSort {
field: CustomerSortField!
direction: SortDirection! = ASC
}
enum CustomerSortField {
id
}
type Query {
# ...
customer(id: ID!): Customer!
customers(
offset: Int! = 0
limit: Int! = 25
search: String
filter: CustomerFilter
sort: [CustomerSort!]
): PaginatedCustomers!
}
input CustomerInput {
firstName: String!
lastName: String!
}
input CustomerUpdateInput {
firstName: String
lastName: String
}
type Mutation {
# ...
createCustomer(input: CustomerInput!): Customer!
updateCustomer(id: ID!, input: CustomerUpdateInput!): Customer!
deleteCustomer(id: ID!): Boolean!
}
The schema should already be available when you start the GraphQL Playground locally http://localhost:4000/api/graphql, and you should be able to play around with the queries.
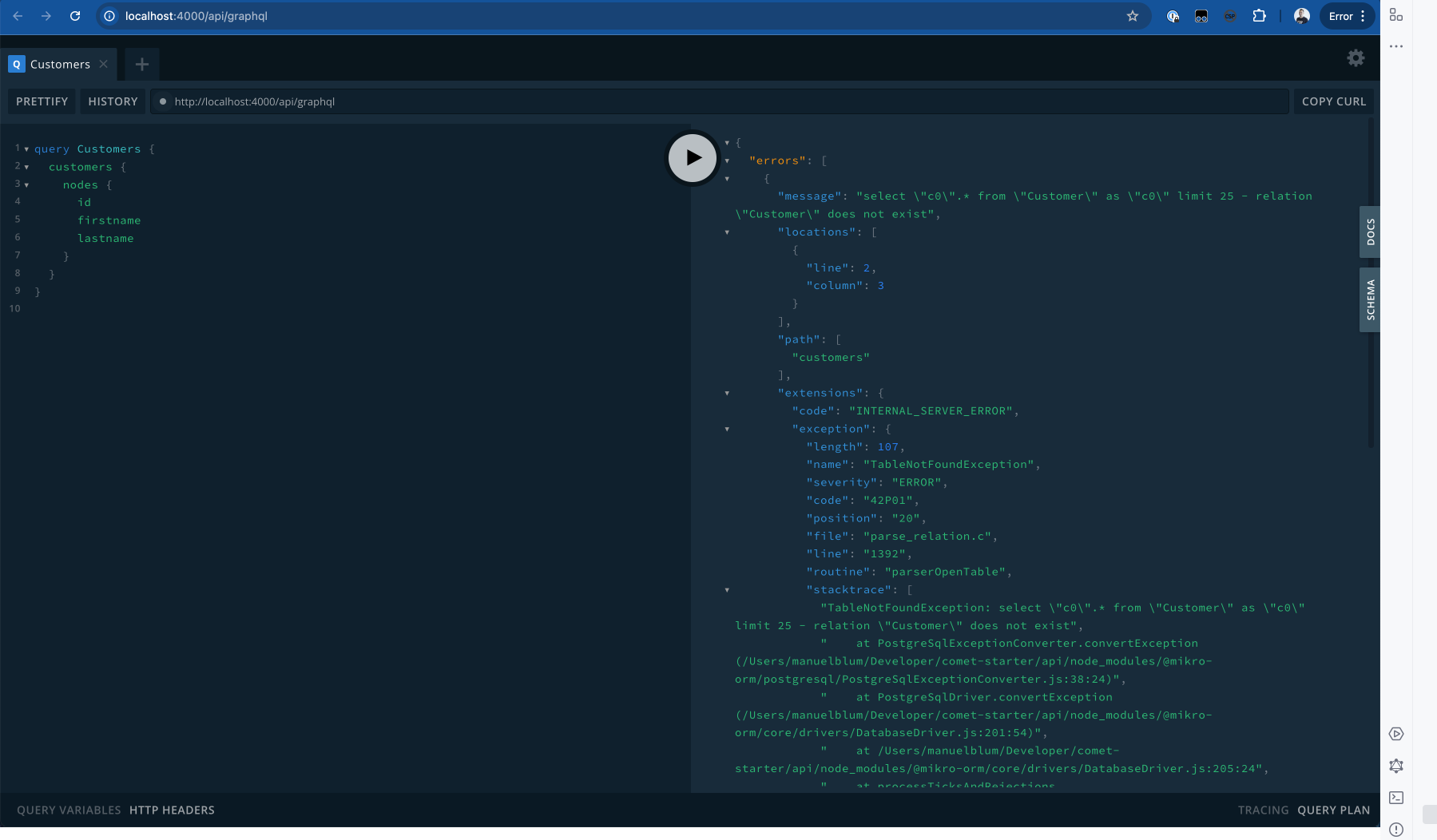
As soon as you start to execute the first Query, you will see that MikroORM will throw an error, stating that the Customer Table does not exist in the Database.